India’s Vision: Achieving Smartphone Self-Sufficiency by FY25
India is embarking on an ambitious journey to achieve complete smartphone self-sufficiency by the end of the fiscal year 2025 (FY25). This strategic initiative aims to reduce reliance on imports, enhance local manufacturing capabilities, and position India as a global hub for smartphone production. As the country works towards this goal, it is expected to reshape the landscape of the tech industry and promote economic growth.
Key Highlights
- Statistical Insight: In FY23, imported smartphones made up 4.2% of the market; by FY25, this will drop to 0.25%.
- Major Players and Companies: like Samsung, Oppo, Vivo, and Xiaomi already manufacture in India, with Apple and Google now joining the push for self-sufficiency.
- Price Impact: Apple’s local production of high-end models could reduce the cost by around ₹15,000.
- Future Targets: India’s electronics sector aims for $500 billion in production, largely driven by the government’s Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme.
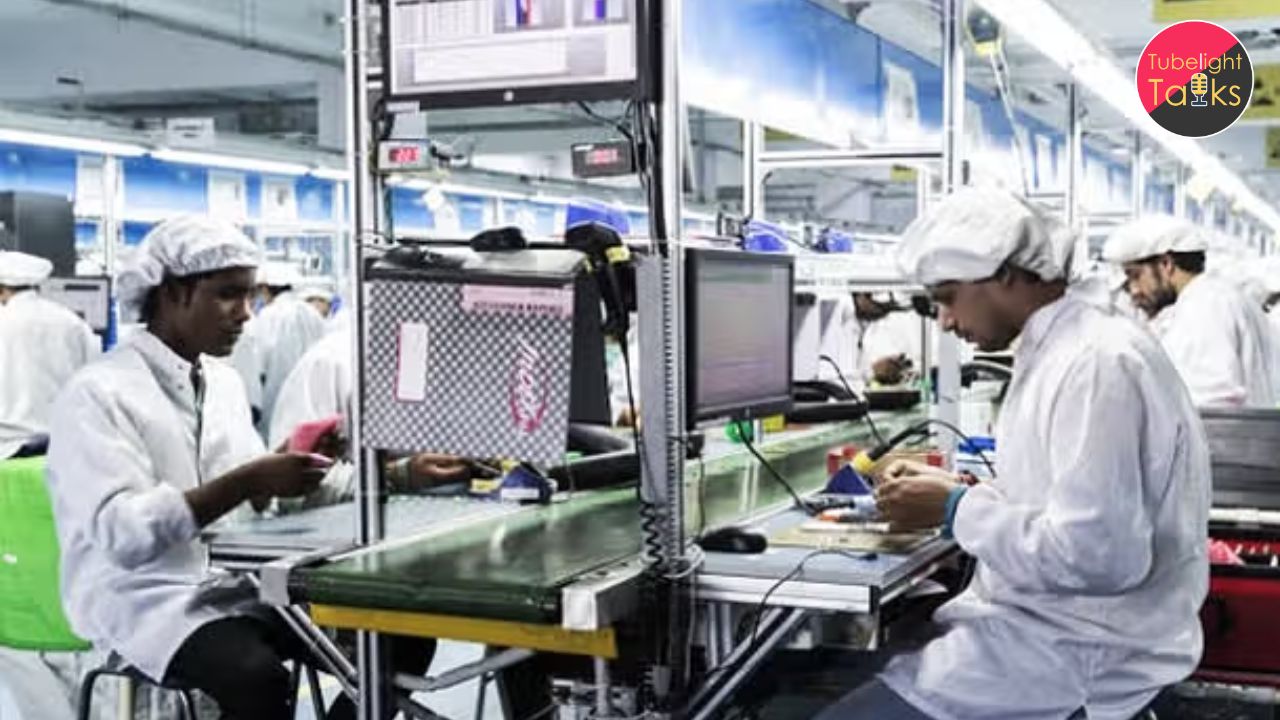
Current Landscape of Smartphone Manufacturing in India
Historically, India has been a significant market for smartphones, but the majority of high-end devices have been imported. In FY23, imported smartphones constituted 4.2% of the market, which reduced to 2.5% in FY24. However, projections indicate that this figure could drop dramatically to just 0.25% by FY25. This shift is driven by several factors, including government initiatives, increased investments from major tech companies, and a rising demand for locally manufactured devices.
Key Players and Initiatives
Major global brands such as Apple and Google are already investing in local manufacturing. Recently, Apple began assembling its flagship iPhone Pro and Pro Max models in India, while Google announced plans to manufacture its Pixel series, specifically the Pixel 8, within the country. These developments mark a pivotal shift in how international companies perceive the Indian market, signaling confidence in its manufacturing potential.
In addition, domestic companies like Samsung, Oppo, Vivo, and Xiaomi have established significant manufacturing operations in India. Their continued investment will be critical in ensuring that a wide range of smartphones, from budget to premium models, are produced locally.
Government Support: The PLI Scheme
The Indian government’s Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme, launched in FY20, aims to boost local manufacturing and attract global players. This program incentivizes companies to increase their production levels in India, thereby creating jobs and enhancing technological capabilities. The government has set a target of $500 billion in electronics production, which includes a focus on smartphones.
To further support this initiative, the FY25 budget is expected to reduce customs duties on smartphone imports, targeting the grey market for high-end phones. This reduction is likely to benefit consumers through lower prices while encouraging manufacturers to produce more locally.
Economic and Market Implications
Achieving smartphone self-sufficiency will have several positive implications for the Indian economy:
1. Cost Reduction: The local manufacturing of smartphones will likely lead to a decrease in the prices of high-end devices. With lower import costs, brands like Apple could reduce their iPhone prices by 3-4%, making premium smartphones more accessible to Indian consumers.
2. Job Creation: The expansion of manufacturing facilities will create numerous job opportunities across various sectors, from assembly line workers to supply chain managers and technical support staff.
3. Technology Transfer and Innovation: As international companies invest in local manufacturing, there will be a transfer of technology and skills, fostering innovation and the development of new technologies in India.
4. Increased Global Competitiveness: With a focus on high-quality production, India can emerge as a competitive player in the global smartphone market, attracting more investments and boosting exports.
India’s vision by FY25
Achieving smartphone self-sufficiency by FY25 is not just an economic goal; it represents a significant shift in the country’s technological landscape. By investing in local manufacturing and reducing dependence on imports, India is poised to become a leader in the smartphone industry. As major brands align their strategies with this vision, the future looks promising for both consumers and the economy.
Technology and Spirituality:Why Only in Kalyuga?
In Kalyuga, the last of the four yugas, we witness unprecedented advancements in technology that have transformed our lives. This era holds a unique significance as it serves as a gateway to deeper spiritual understanding. According to Tatavdarshi Sant Rampal Ji Maharaj ji, true spiritual knowledge is essential for attaining salvation, and Kalyuga provides us with the tools to access this knowledge like never before.
In this digital age, the teachings of Sant Rampal Ji Maharaj ji resonate more than ever, spreading through various platforms to reach a wider audience. He emphasizes that despite the distractions of modern life, technology can be a powerful ally in our spiritual journey, allowing seekers to explore and connect with authentic spiritual wisdom.
To embark on this transformative journey and to gain insight into true spiritual teachings, you can easily find Sant Rampal Ji Maharaj’s discourses across all digital platforms. Simply search for “Sant Rampal Ji Maharaj” on any social media or video-sharing platform to discover the guidance that can lead you toward spiritual enlightenment and salvation.
FAQs:
1. What is the full form of PLI?
Production Linked Incentive
2. When was the PLI scheme launched?
2020
3. What was the size of India’s smartphone market in 2023?
$33 billion
4. Expected market size in 2024?
$37 billion
5. Full form of ICEA?
Indian Cellular and Electronics Association









Discussion (0)