The Power Behind Space Exploration: How Rocket Engines Work
How Rocket Engines Work: Rocket engines are the backbone of space exploration, enabling spacecraft to escape Earth’s gravity and venture into the vast unknown. These powerful machines have fascinated humans for decades, with their technology undergoing significant advancements over the years. In this article, we’ll delve into the workings of rocket engines, explore their various types, and discuss how they have revolutionized space exploration.
How Rocket Engines Work
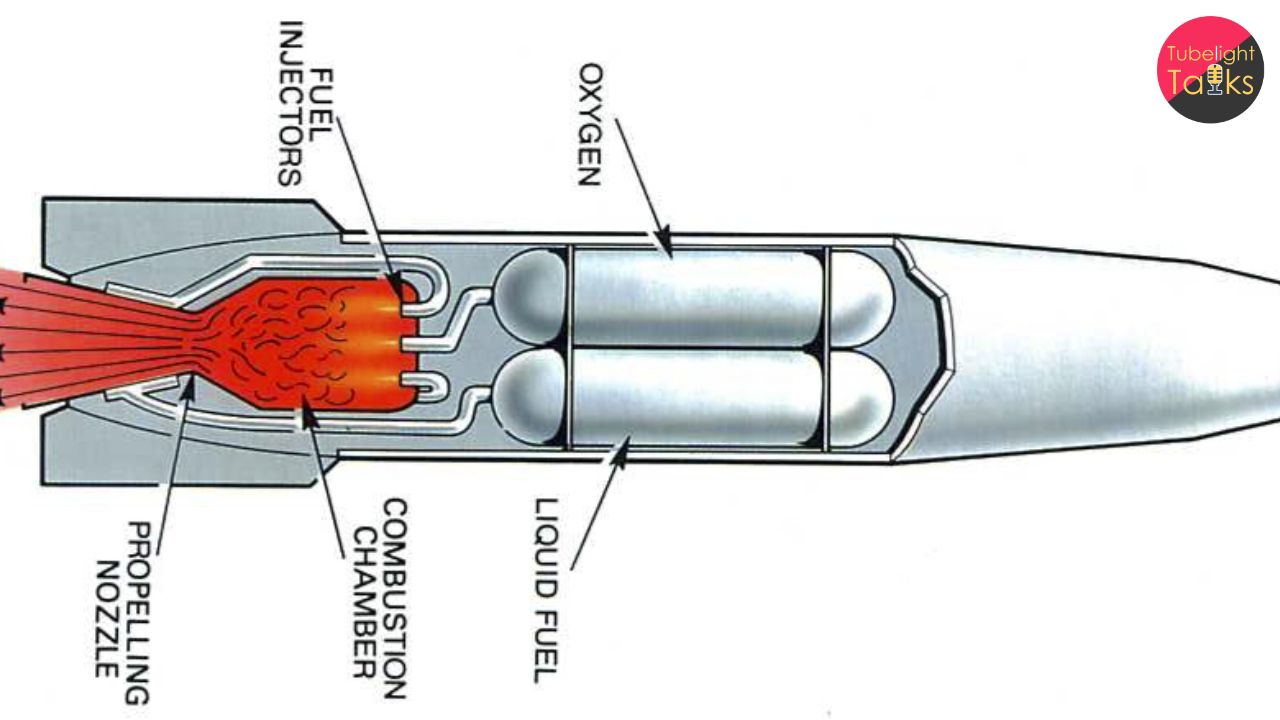
A rocket engine is a type of jet engine that uses the principle of conservation of momentum to generate thrust. The basic components of a rocket engine include:
- Combustion Chamber: Where the fuel and oxidizer are burned to produce hot gases.
- Nozzle: Expels the hot gases, accelerating them to high speeds and producing thrust.
- Fuel and Oxidizer: The propellants burned in the combustion chamber to generate thrust.
The process works as follows:
- The fuel and oxidizer are pumped into the combustion chamber.
- The propellants are burned, producing hot gases.
- The hot gases are expelled through the nozzle, accelerating to high speeds.
- As the gases exit the nozzle, they produce a reaction force that propels the rocket forward.
Types of Rocket Engines
How Rocket Engines Work: Several types of rocket engines exist, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Some of the most common types include:
- Liquid-Fueled Rocket Engines: These use liquid fuel and oxidizer, which are pumped into the combustion chamber. Examples include the Saturn V rocket that took astronauts to the Moon.
- Solid-Fueled Rocket Engines: These use a solid fuel and oxidizer cast together in a single block. Examples include the Space Shuttle’s solid rocket boosters.
- Hybrid Rocket Engines: These combine solid and liquid fuels. An example is SpaceShipOne, which won the Ansari X Prize.
- Nuclear Rocket Engines: These use nuclear reactions to produce thrust. An example is NASA’s Nuclear Engine for Rocket Vehicle Application (NERVA) program.
- Electric Rocket Engines: These use electricity to accelerate charged particles, such as ions or electrons, to produce thrust. An example is NASA’s Deep Space 1 spacecraft.
How Rocket Engines Have Made Space Exploration Easier
How Rocket Engines Work: Rocket engines have played a crucial role in space exploration by enabling spacecraft to travel faster, farther, and more efficiently. Some of the ways they have facilitated space exploration include:
- Increased Payload Capacity: Modern rocket engines allow spacecraft to carry more cargo, including crew members, scientific instruments, and communication equipment.
- Improved Efficiency: Advances in technology have enhanced efficiency, enabling spacecraft to travel farther with less fuel.
- Reduced Launch Costs: Reusable rocket engines, such as those developed by SpaceX, have significantly lowered launch costs, making space travel more accessible.
- Enhanced Reliability: Modern rocket engines are more reliable, reducing the risk of launch failures and ensuring safer journeys for spacecraft.
Conclusion
How Rocket Engines Work: Rocket engines are the foundation of space exploration, enabling humanity to escape Earth’s gravity and venture into the vast unknown. With their powerful technology, rocket engines have made space exploration faster, easier, and more efficient. As we continue to push the boundaries of space travel, rocket engines will remain a vital component of our exploration efforts.










Discussion (0)